Orthopedic Knee Surgery
Non-Operative Knee Treatment Options
Medications
- Wide array of non-surgical pain management medications
- Post-operative recovery medications available
- Personalized medication discussions during office visits
- Tailored solutions for your specific needs
Injections
- Various knee pain-reducing injections available
- Functions range from anti-inflammatory to joint surface smoothing
- Options include hyaluronic acid, cortisone, and Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
- Injection selection discussed during office visits for personalized care
Physical Therapy
- Range of motion and muscle-strengthening exercises
- Stabilization and enhanced knee mobility
- Pain reduction through improved mobility
- Integral part of post-total knee replacement surgery
- Crucial for a successful outcome after knee replacement

Operative Knee Treatment Options
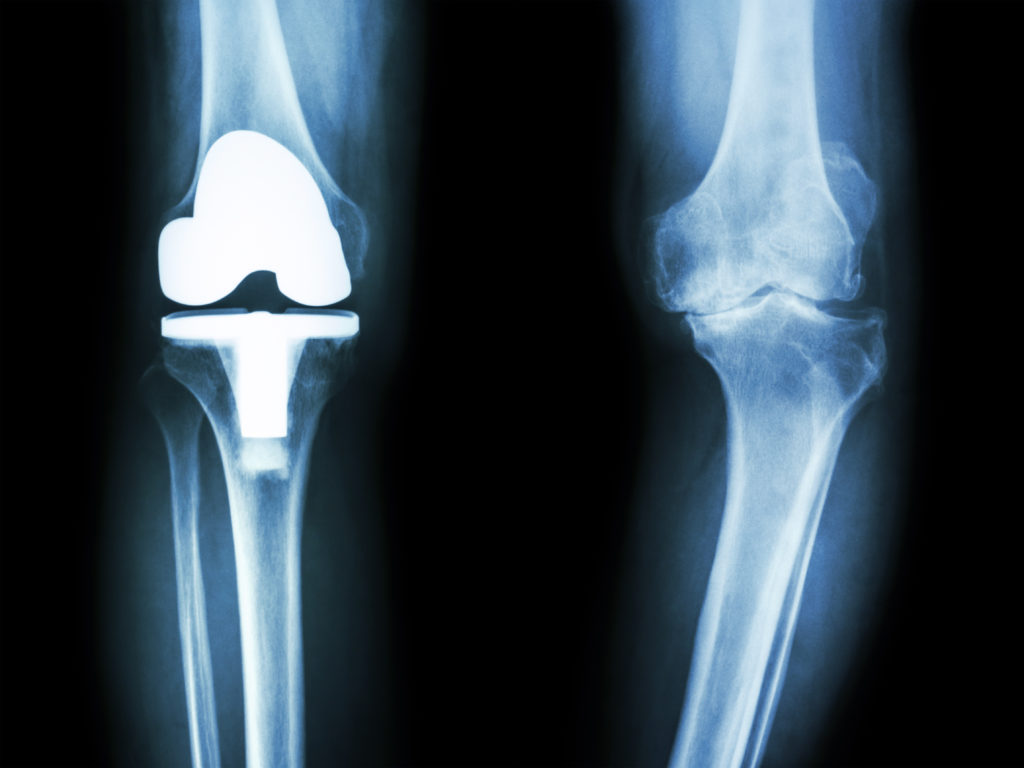
Total Knee Replacement
When knee pain continues to persist even with non-operative treatments, it may become necessary to undergo a total knee replacement surgery.
- Beneficial when the knee joint has worn down to the point where the joint is no longer sliding smoothly.
- Surgery involves removal of damaged knee parts
- Implants selected to recreate smooth joint surface
- Typically a 1.5-hour procedure
- Can be performed as an outpatient surgery so you can go home the same day and sleep in your own bed
Revision of A Total Knee Replacement
- Implants are designed for long-lasting use (typically 10-20 years)
- Rare but there is a possibility of wear or failure
- Increased risk when overweight or involved in high-impact activities
- Revision surgery needed when knee replacement fails
- Procedure involves replacing old device with a new one
- Revision surgeries require more planning, specialized tools, and surgical skill
- Surgery time for revision: 2-3 hours, compared to 1.5 hours for primary replacement

